Disclosing the Mysteries: The Rise and Downfall of Dark Web Markets
from web site
Lately, the dark web has fascinated people's minds, often evoking images of anonymous transactions, forbidden items, and a concealed underworld existing past the reach of traditional law enforcement. Among the most infamous aspects of this dark landscape are dark web markets, sites that support the exchange of a range of narcotics to forged papers. As society becomes more and more digital, these markets have transformed, showcasing both the creativity and challenges of the underground economy.
However, the rise of dark web markets is accompanied by their inevitable fall. Law enforcement agencies worldwide have increased efforts to break into and take down these platforms, resulting in considerable crackdowns that have sent shockwaves through the cyber underworld. The ongoing cat-and-mouse game between authorities and users has shaped the dynamic landscape of the darknet, revealing a complex interplay of secrecy, protection, and risk. As we explore further this topic, we will examine the roots, progress, and persistent issues faced by dark web markets, highlighting a intriguing yet troubling aspect of today's world.
Grasping the Hidden Web
The dark web is a segment of the internet that is not indexed by standard search engines. It exists on an secure network, requiring specific software such as Tor to enter it. This concealed nature allows users to function anonymously, making it a haven for various activities, both legal and criminal. While many may link the dark web primarily with forbidden commerce, it also serves as a platform for free speech and confidentiality, especially in countries with restrictive governments.
Entering the deep web requires using dedicated tools that secure users' personal information. The most common of these tools is the Tor web browser, which shields internet traffic and routes it through multiple servers. This creates a layer of anonymity for users, protecting them from watchfulness and tracing. Despite its notoriety, the hidden web also contains forums, communities, and even marketplaces focused on lawful interests, such as privacy advocacy and social justice.
The paradox of the dark web presents a complex picture. On one hand, it is notorious for facilitating the exchange of controlled substances, illegal arms, and stolen data; on the other, it provides a safe space for leakers and those seeking to communicate freely without worry of state interference. Understanding this intricate landscape is crucial for understanding the broader implications of internet security, protection, and the ongoing battle between law enforcement and the forces that function in shadowy areas of the internet.
The Evolution of Underground Markets
Darknet markets have seen considerable transformations since their their beginnings in the late 2000s. Initially, these platforms were primitive and underdeveloped, primarily operating through discussion boards and basic messaging spaces where individuals would trade goods and services lacking any structured interface. The discretion offered by the darknet attracted a targeted audience looking to accessing products that were commonly illegal or difficult to obtain through mainstream means. Prominent early examples include Silk Road, which set the stage for future markets by utilizing Bitcoin as a means of exchange, enhancing the confidentiality of its users.
As cybersecurity steps increased and law enforcement began to enforce regulations on early markets, darknet markets developed into more advanced entities. This evolution led to the creation of intuitive interfaces and advanced escrow systems that bolstered confidence and protection among clients. Rivalry among markets encouraged innovation, resulting in capabilities like customer ratings, seller authentication, and item evaluations. These advancements not only refined the shopping experience but also attracted a wider audience, fostering a sense of community among participants who valued the anonymity that darknet markets provided.
Nonetheless, the rise of these markets also initiated a cycle of law enforcement intervention. Significant operations to dismantle major platforms, such as the takedown of the Silk Road in the year 2013, showcased the vulnerabilities inherent in the darknet infrastructure. Despite these efforts, novel markets quickly surfaced to fill the void, often implementing stronger security measures and using decentralized architectures to evade detection. This ongoing battle between innovation in darknet market operations and law enforcement tactics illustrates a nuanced dynamic, making the evolution of darknet markets a continuously unfolding narrative.
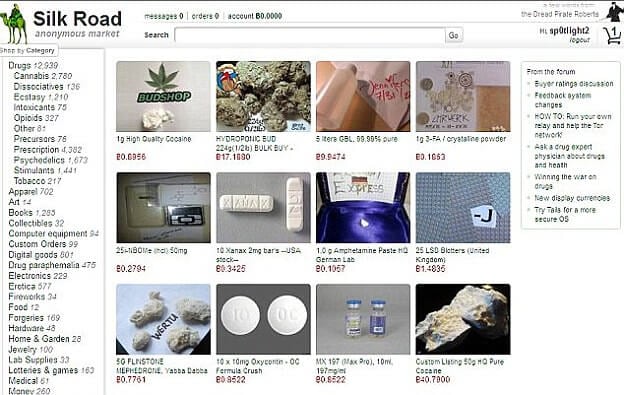
A Downturn and Outlook of Shadow Net Trade
The decrease of shadow net markets can be linked to various factors, including increased police initiatives and heightened scrutiny from cybersecurity professionals. As authorities around the world have intensified efforts to dismantle major sites, many have found it progressively hard to operate without the ever-present danger of a raid or detainment. Notable takedowns such as Silk Road and Alpha Bay served as critical milestones, instilling a sense of apprehension within the shadow net environment and dissuading new vendors from joining the platform. Additionally, the reluctance of participants to have faith in emerging sites, often plagued by scams or security breaches, has further added to the decline.
Despite the obstacles faced by operating platforms, there still exists a significant desire for services and offerings that the underground provides. This demand may help maintain lesser-known, more targeted services that work under a lesser profile. Cutting-edge solutions, such as non-centralized options and improved privacy systems, could renew interest and utilization of shadow net sites. As long as there are people seeking privacy for various reasons, from safety factors to illicit actions, the potential for shadow net commerce will always remain, albeit in a changed form.
Looking ahead, the future of dark web business is anticipated to pivot towards increased decentralization and fusion of distributed ledger technology. The rise of digital currencies has offered a more safe way of exchange that is appealing to users trying to keep privacy. As the scene changes, new commerce formats may adopt decentralized monetary systems, making these services less likely to close and regulate. While the fall of old-school underground markets may signify the conclusion of an epoch, it creates opportunities to new options that could reshape how commerce occurs in the shadows.
