Bedside monitoring of blood beta-hydroxybutyrate levels in
from web site
Post-Exercise Changes of Beta Hydroxybutyrate as a for Beginners

Beta Hydroxybutyrate, Ketones, Diabetic Ketoacidosis Labs.

Tracking treatment for diabetic ketoacidosis Examining the differential medical diagnosis of any client presenting to the emergency room with hypoglycemia, acidosis, suspected alcohol intake, or an unexplained boost in the anion gap In pediatric clients, the presence or absence of ketonemia/uria is an important component in the differential diagnosis of innate errors of metabolic process Serum beta-hydroxybutyrate is a key criterion monitored during regulated 24-hour fasts Beta-hydroxybutyrate ( BHB ) is 1 of 3 sources of ketone bodies.
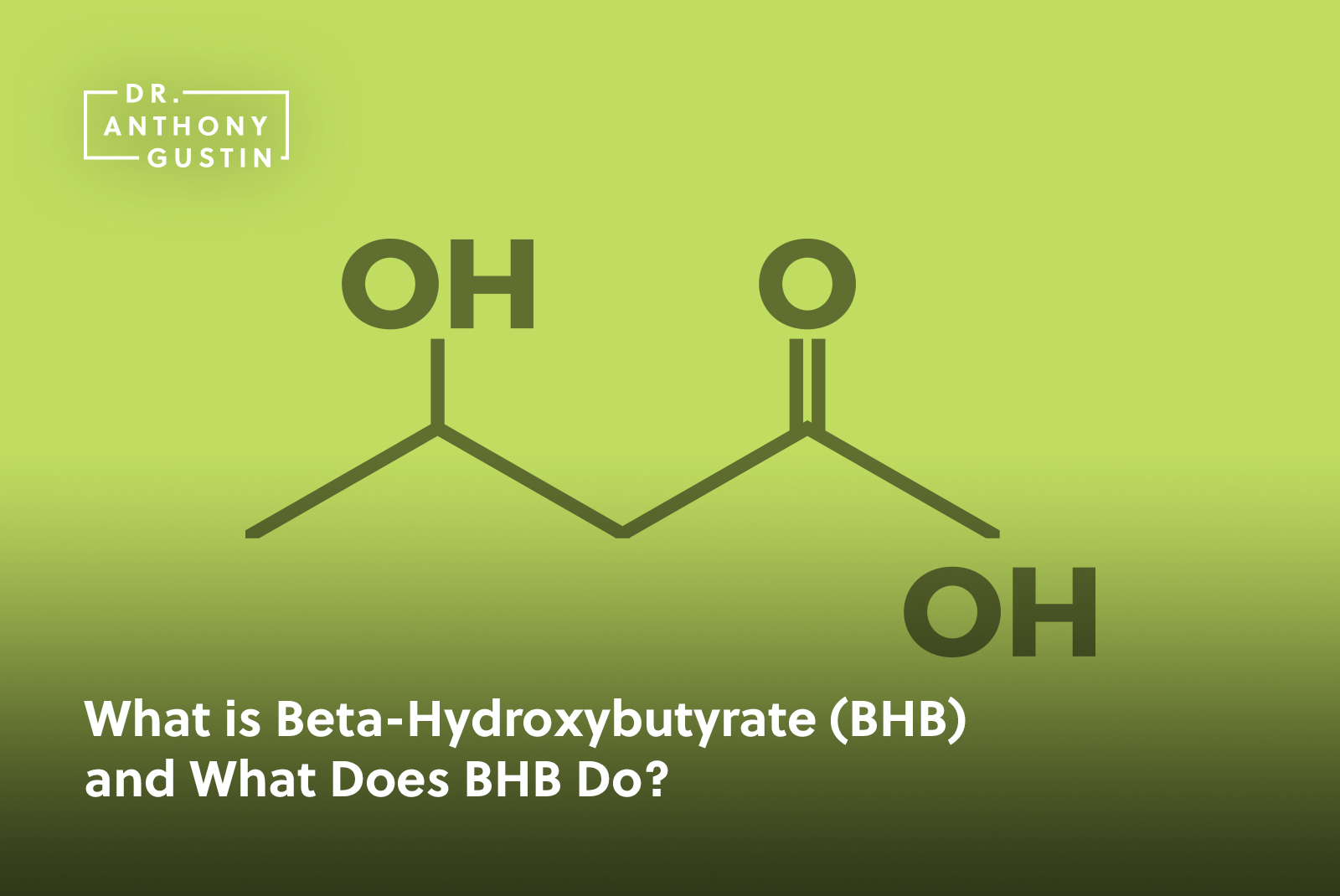
The Association Between Serum β-hydroxybutyrate and Can Be Fun For Everyone
During carb deprivation (starvation, digestive disturbances, regular vomiting), reduced carbohydrate utilization (diabetes mellitus), glycogen storage illness, and alkalosis, acetoacetate production increases. The increase might exceed the metabolic capability of the peripheral tissues. As acetoacetate collects in the blood, a percentage is transformed to acetone by spontaneous decarboxylation. The remaining and higher portion of acetoacetate is converted to BHB.
Serum BHB increases in response to fasting, however ought to not exceed 0. 4 mmol/L following an over night fast (approximately 12 hours). In pediatric patients, a hypo- or hyper-ketotic state (with or without hypoglycemia) may recommend specific groups of metabolic disorders. Twenty four-hour fasting tests need to not be carried out in clients
