Some Of Continental Electric Motors
from web site

Not known Facts About WEG Electric Motors - HECO All Systems Go - HECO Inc.
An electrical motor is a device that converts electrical energy into power. For an electric motor, electric power from a battery or grid is input into the motor, and power is output in the kind of a rotating shaft. As soon as merely a scientific toy, electrical motors are found today inside whatever from power tools to elevators to toothbrushes to when again toys.
Modern civilization would actually grind to a stop without electrical motors. The future guarantees roadways dominated by electric cars and factories staffed by robots whose motions are impelled by electric motors. A standard understanding of electrical motors is essential for their correct application. While all electric motors offer the exact same basic function of converting electrical energy to power, the technique by which they transform the energy can vary considerably.
In 1821, Michael Faraday used electrical power from a battery to cause a wire to circle a magnet in a pool of mercury. A similar experiment was carried out in 1822 by Peter Barlow, utilizing a star-shaped wheel called a Barlow Wheel, which dipped its suggestions into mercury as it turned.

The Greatest Guide To Electric Motor manufacturers & suppliers - Made-in-China.com
In 1837, Thomas Davenport acquired the first patent for an electric motor intended for industrial usage. Davenport was a man ahead of his time, and while his style was sound, it was just long after his patent expired that batteries and electrical grids were developed to financially power his motor.
The early creators have been followed by many other innovators and innovators, improving the efficiency and effectiveness of electric motors. Check Here For More H2W Technologies, Inc. Electric Motors H2W Technologies, Inc. Electric Motors H2W Technologies, Inc.
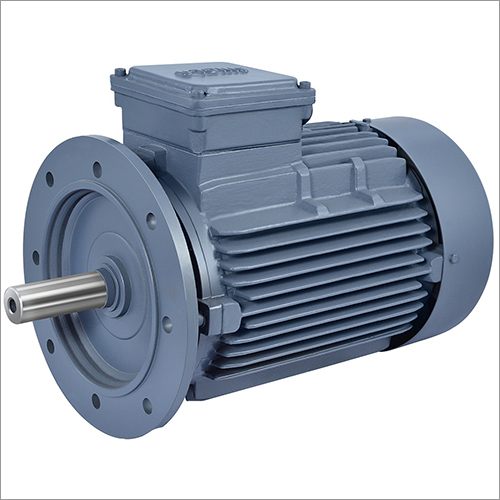

Electricity is the motion of electrons from atom to atom within a carrying out medium such as a wire. Early experimenters considered electricity as a 'fluid' with attributes corresponding to a liquid flowing through pipes. Modern technicians, electrical contractors, and engineers still find this example beneficial. In this fluid analogy, electrical charge is a step of the quantity of electrical 'fluid,' voltage is a procedure of electrical pressure and current is a measure of electrical flow rate.
