Top Guidelines Of A hair transplant can give you permanent, natural-looking results
from web site
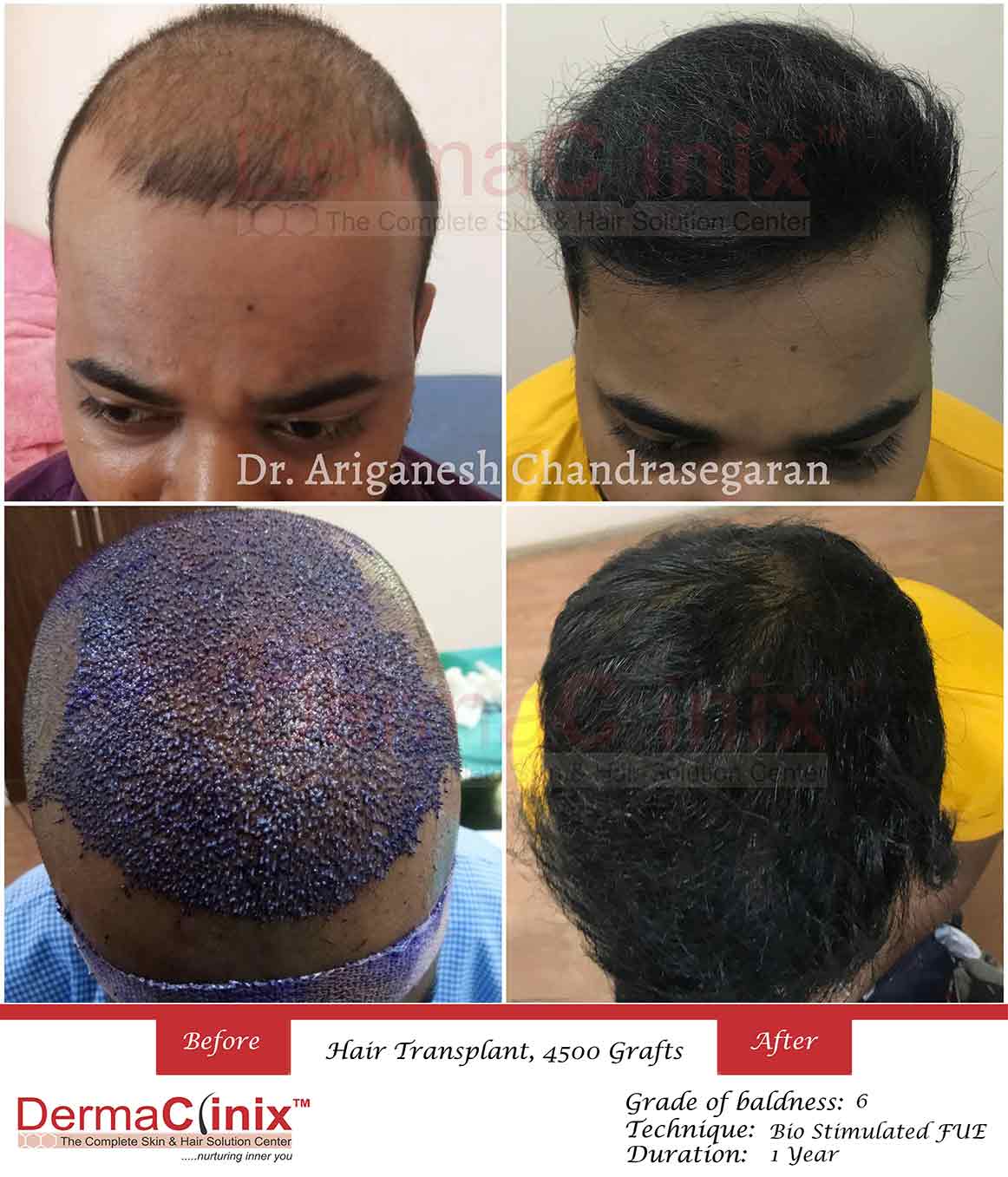
The 4-Minute Rule for Hair transplant: Costs, recovery, and what to expect
What is the distinction between female and male pattern hair loss? Androgenic alopecia is the kind of loss of hair that impacts guys and ladies. It is triggered by a hereditary predisposition to the hormonal agent Dihydrotestosterone (DHT). When This Is Noteworthy rise, the hair follicles shrivel and hair development lessens. However, guys and females normally have various reactions to DHT and therefore different patterns of loss of hair.
If left untreated, hair loss can advance to baldness due to the eventual death of hair roots in these areas of the scalp. For the majority of men, the side and back of the head are less impacted by DHT. On the other hand, female pattern hair loss begins with thinning hair throughout the main location of the scalp and progresses outward if not treated.
Just a small number of females will experience prevalent baldness. What medical conditions trigger hair loss? There are a number of medical conditions or illness that cause hair loss in both males and females. These consist of: thyroid disease, anemia, lupus, protein shortage, polycystic ovary syndrome and low vitamin levels. How is hair loss managed clinically? Although hair transplantation surgery is the most permanent and efficient medical treatment for loss of hair, there are also methods to clinically handle hair loss without surgery.
Some Known Details About Hair Transplantation - an overview - ScienceDirect Topics
Hair loss can likewise be dealt with by handling an underlying median condition in some clients. Dr. Stong will carefully listen to your treatment goals and examine your hair loss condition before suggesting the most efficient surgical or non-surgical treatment alternatives that are offered to you. It is necessary to comprehend that many hair loss treatments need ongoing upkeep treatment for enduring results.


It was originally developed as an antihypertensive medication. Minoxidil does not work for everyone, but it can stop the progression of male pattern balding and stimulate brand-new hair development in some people. This kind of non-surgical loss of hair treatment is best for more youthful clients who have the beginning indications of loss of hair.
Unfortunately, A U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) analysis of unfavorable occasion data revealed widespread reports of male sexual dysfunction as an adverse effects of otherwise healthy Propecia users ages 21 to 46. Beyond its sexual side impacts, in a very little number of patients the sexual adverse effects can be long-term.
