Conducting a Light Rights Assessment: Procedure
from web site
Within the realm of property development, understanding the nuances of light rights can significantly influence the outcomes of projects. A survey for Right to Light is an integral process that assesses how much natural light reaches a property and helps developers traverse the complex legal landscape surrounding light rights. With the increase in urban development and growing competition for space, ensuring that your project respects the rights of pre-existing structures has never been more important.
This piece will guide you through the detailed process of conducting a Right to Light survey, showcasing its importance in avoiding potential disputes and guaranteeing compliance with zoning laws. From learning about your legal rights to examining the tools and techniques used in these surveys, we will delve into the fundamental aspects that every developer should know. Whether you are embarking on an extension or a new build, being informed about Right to Light can protect your project and foster positive relationships with neighboring properties.
What Is a Right to Light Survey?
A Light Rights Assessment is an assessment conducted to determine the availability and quality of natural light that adjacent properties receive. It is an important process, particularly in city areas where recent developments may interfere with light to existing buildings. The survey assesses how planned constructions may impact sunlight to adjacent properties, helping to educate both developers and property owners about prospective legal rights and consequences.
During the survey, multiple factors are considered, including the direction of the buildings, closeness to adjacent structures, and pre-existing light situations. This involves measuring angles and spacings to find out how much light reaches each property. Right To Light Addington from the survey play a vital role in decision-making processes for development, ensuring that any upcoming construction adheres with legal rights to light established under UK law.
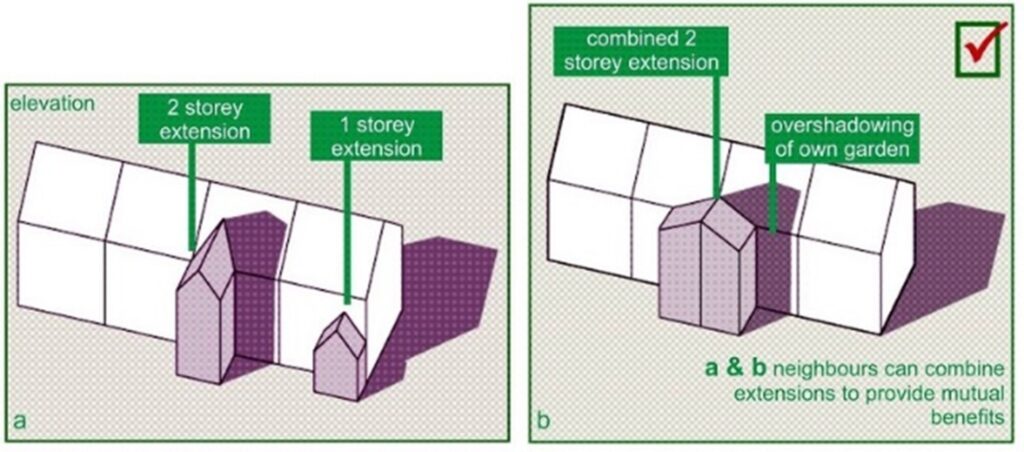
In conclusion, a Right to Light Survey serves as a forward-looking measure to identify possible issues before they happen in the development process. By understanding light rights and how they may be influenced, stakeholders can navigate the intricacies of property development while reducing the chance of arguments with neighbors over light access.
Understanding Your Lawful Entitlement to Illumination
The legal right to light is an essential aspect of property ownership and development in the UK. This right typically allows a property owner to obtain natural light through specific apertures, such as windows, without inhibition from nearby buildings or structures. The law comes into play primarily under the Prescription Act 1832, which establishes that if a property has received light for an unbroken period of 20 years, the owner can request a judicial right to maintain having that light.
Comprehending this right is crucial for both property developers and property owners. For developers, it is important to consider pre-existing rights to light when planning new developments. Ignoring these rights can lead to litigation and costly delays. Property owners, on the other hand, may seek to protect their light rights from neighboring developments that endeavor to obstruct or considerably reduce the light they currently enjoy. Clarity on these rights can help traverse the often complex landscape of zoning regulations.
In addition to legal rights, legal agreements may also affect light rights in certain developments. Property transactions can feature clauses related to rights to light, which may provide additional protections or obligations. Therefore, it is wise for all stakeholders involved in property development or acquisition to completely understand both their statutory rights and any contractual commitments to guarantee adherence and protect their interests effectively.
How a Right to Light Survey Is Conducted
Carrying Out a Right to Light survey involves a systematic approach to assess the likely impact of a proposed construction on the natural light available to neighboring properties. Initially, surveyors assemble necessary information about the site, such as current structures, their altitudes, and positions in relation to the neighboring properties. This typically includes reviewing planning documents and relevant historical data that might influence light access. Comprehending the context of the location is vital, especially in urban areas where buildings are densely packed.
Once the initial data is collected, surveyors employ specialized tools and techniques to analyze light availability. This typically involves the use of software that follows the Building Research Organization (BRE) guidelines, which provide a structure for evaluating whether a proposed development will substantially reduce light levels to affected properties. Surveyors may also use 3D modeling to precisely simulate light conditions and depict the possible impacts of the new developments. The findings are meticulously documented to ensure transparency and accuracy.
At last, surveyors produce a thorough report outlining their findings and recommendations. This report details any potential right to light infringements, giving insights into how they could be mitigated. It serves as an important resource not only for developers contemplating new projects but also for neighbors concerned about their light rights. The in-depth nature of the report ensures that all parties engaged have a clear understanding of the implications and can take informed decisions moving forward.
